College Board Concepts
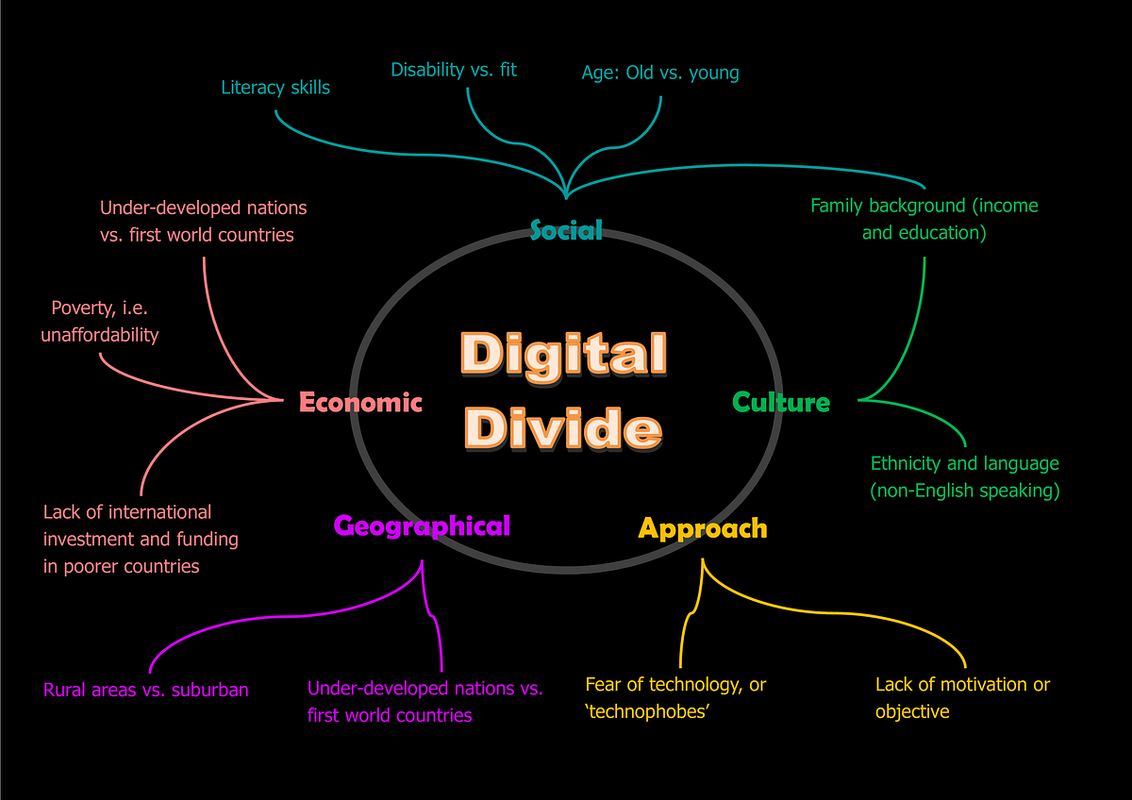
1.C.1: Internet access varies between three main groups: demographic, socioeconomic, and geographic categories; as well as countries
1.C.2: “Digital Divide” refers to differing access to computing devices and the Internet based on the three groups stated above
Demographics include age, religion, race, etc
Some countries: Computers not common rurally Only small number of websites, also those that are permitted by govt
Internet is used to protect and advocate the government
High level of internet surveillance
1.C.3: Can affect multiple groups and also individual
1.C.4: Raises questions about issues of equity, access, and influence both globally and locally
1.C.5: Digital divide is affected by the actions of individuals, organizations, and governments Discuss positive solutions to digital divide
Welcome to today’s lesson on the digital divide! We’ll explore how disparities in technology access impact individuals and societies, and what can be done to bridge these gaps.
Digital Divide Definied: The digital divide refers to the gap between individuals, communities, or countries that have access to modern information and communication technology (ICT) and those that do not. This divide can manifest in various forms, including differences in access to the internet, availability of computers and other digital devices, and the ability to use and benefit from digital resources.
The divide exists in two main dimensions: access and usage . Access involves the availability of internet and devices, while usage looks at how people utilize technology. Both dimensions contribute to the overall digital inequality.
Internet access varies between three main groups: demographic, socioeconomic, and geographic categories; as well as countries.

Demographics include age, race, religion, etc. These different groups have different access to CS and technology.
Economic disparities: Individuals without access to digital technologies may find it challenging to participate in the modern economy, access online job markets, or acquire the digital skills needed for high-demand professions. This can lead to a perpetuation of existing socioeconomic gaps and hinder social mobility.
Educatioinal disparities: Students without access to these resources may fall behind in terms of academic achievement and miss out on the benefits of interactive and technology-enhanced learning experiences.
Geographical disparities: Rural and remote areas may lack the necessary digital infrastructure, leading to limited access to broadband internet and advanced technologies. This can result in isolation from economic opportunities, education, and healthcare services available online.
Elderly disparities: Older individuals may experience challenges in adopting and adapting to new digital technologies. The lack of digital literacy among the elderly can lead to social isolation, limited access to healthcare information, and difficulties in participating in online activities.
The digital divide is often linked to broader socioeconomic disparities. Individuals with higher incomes and better educational backgrounds may be more likely to have access to and utilize digital technologies compared to those with lower socioeconomic status.
In easy terms... an example would be that Higher-income individuals have more accessibility to the newest tech which lets them access technology before other people.

Innovation Gaps
Issue:
Access to digital technologies is a key driver of innovation. Communities and nations that lack access to advanced digital infrastructure may miss out on opportunities for technological advancements and innovation. This contributes to a widening gap between technologically advanced and less developed regions, impacting economic growth.
Productivity Losses:
Issue:
Businesses and workers with limited access to digital tools may experience lower productivity compared to their digitally connected counterparts. This is particularly relevant in industries where digital technologies enhance efficiency, collaboration, and innovation.
Digital Skills Gap:
Issue:
The digital divide contributes to a digital skills gap, where a portion of the population lacks the skills necessary for contemporary workplaces. This gap can hinder workforce productivity, limit employability, and reduce the overall competitiveness of a nation’s workforce.
Reduced Access to Financial Services:
Issue:
Digital technologies have revolutionized financial services, offering convenient and accessible banking solutions. However, individuals without digital access may struggle to access basic financial services, hindering their ability to save, invest, and participate fully in the financial system.
Global Competitiveness Impact:
Issue:
Nations that do not address the digital divide may find themselves at a disadvantage in the global marketplace. A lack of digital infrastructure and skills can impede a country’s competitiveness in industries driven by technology and innovation.
Geographic issues play a significant role in the digital divide, contributing to disparities in digital access and connectivity across different regions. Here are key points to consider when discussing the geographic aspects of the digital divide:
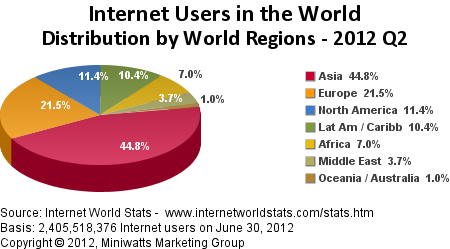
Rural-Urban Disparities:
One of the prominent geographic issues in the digital divide is the disparity between rural and urban areas. Urban centers often have better digital infrastructure, including high-speed internet and access to advanced technologies, while rural areas may lack these resources. This urban-rural gap hinders equal participation in the digital economy and limits access to online educational and healthcare resources in rural communities.
Limited Infrastructure in Remote Areas:
Remote and isolated areas face challenges in establishing and maintaining digital infrastructure. Building the necessary broadband networks and technology infrastructure in these areas can be cost-prohibitive, leading to limited or no access to high-speed internet and digital services.
Geographical Barriers to Education:
The digital divide impacts educational opportunities based on geography. Students in rural areas may face challenges accessing online learning resources, participating in virtual classrooms, and benefitting from digital educational tools. This creates a knowledge gap between students in urban and rural settings.
Economic Opportunities and Innovation Gaps:
Geographic differences in digital access contribute to disparities in economic opportunities and innovation. Urban centers with robust digital infrastructure are better positioned to attract businesses, foster innovation, and participate in the digital economy, while rural areas may face economic stagnation due to limited connectivity.
Emergency and Disaster Response Limitations:
In times of emergencies or natural disasters, areas with limited digital infrastructure face challenges in communication, coordination, and access to critical information. This can hamper emergency response efforts and exacerbate the impact of disasters on communities.
Global Connectivity Challenges:
On a global scale, some regions face challenges in connecting to the broader internet. Developing countries, especially those in remote or isolated regions, may lack the necessary infrastructure to participate fully in the global digital landscape, impacting economic development and global competitiveness.
How would you attempt to fix the digital divide or prevent it from being as prevalent in our community? What are some things that are already being done? what are some things we can add?
Public libraries are places that help prevent the digital divide in our communities. They offer free internet and technology for those who have limited access.
Answer: Restaurants and cafes could offer internet for free so that people can do work there and have access to internet services.
The impact is widespread, affecting education, employment, and social participation. For instance, the ‘homework gap’ highlights how students without internet access face challenges in completing assignments and accessing educational resources.
Governments, the private sector, and communities play pivotal roles in addressing the digital divide. Initiatives such as broadband expansion and digital literacy programs are crucial steps toward creating a more inclusive digital society.
A seen change: Schools are relying more on technology because the inability to access tech forces underprivileged students to fall behind
Disparities in the availability of content and services online can contribute to the digital divide. Some communities may have limited access to educational resources, job opportunities, or other online services that are crucial for personal and professional development.
Common Negative Effect: The wealthy and those with access to Internet are the ones who can use it. Since tech gives space for many platforms we don’t hear from those who don’t have access to it.
- Internet is used to protect and advocate the government
- High level of internet surveillance
- Can affect multiple groups and also individual
- Raises questions about issues of equity, access, and influence both globally and locally
- Students especially through the pandemic relied on technology to learn
- Those without technology were forced to fall behind
- Those who weren’t connected suffered
- Those without tech cannot easily find jobs
- Stable internet is an important factor for employees
In conclusion, addressing the digital divide is crucial for creating a more equitable society. By understanding its dimensions, causes, and potential solutions, we can work towards a future where everyone has equal access to the opportunities provided by digital technologies.
Organizations provide funding to give tech to those who can’t afford it and also reach out to teach people how to use technology
Links:
Federal Communications Commission (FCC): https://www.fcc.gov/
EveryoneOn: https://www.everyoneon.org/
Code.org: https://www.everyoneon.org/
Digital Promise: https://www.everyoneon.org/
a) A gap between old and new technologies
b) The difference in internet speed between urban and rural areas
c) The gap between those who have access to modern information and communication technology and those who do not
d) The disparity in smartphone ownership
a) Economic status
b) Geographic location
c) Educational background
d) All of the above
a) Bandwidth divide
b) Connectivity gap
c) Net neutrality
d) Broadband barrier
a) Seniors
b) Teenagers
c) College students
d) Middle-aged adults
a) Lack of access to relevant and timely information
b) Too much information available
c) Lack of interest in information
d) Overreliance on traditional media
a) UNESCO
b) FIFA
c) WHO
d) Greenpeace
a) Technological literacy
b) Social media popularity
c) Smartphone brand preference
d) Online gaming skills
a) Digital inclusion
b) Cybernetic equality
c) Virtual unity
d) Tech assimilation
a) North America
b) Europe
c) Sub-Saharan Africa
d) Asia-Pacific
a) Limited access to educational resources
b) Restricted economic opportunities
c) Reduced civic participation
d) All of the above
After you record your answers in this cell, take a screen shot and DM it on Slack to Arushi Pandey & Ananya Asudani (in one message). There will be a penalty of 5% off your grade for each day the assignment is late. The homework will be due Monday December 11th at 11:59 PM.
Answer questions below with solely the letter name! Make sure to have your popcorn hack completed as well.
- [C] Question 1
- [D] Question 2
- [B] Question 3
- [D] Question 4
- [A] Question 5
- [A] Question 6
- [A] Question 7
- [A] Question 8
- [C] Question 9
- [D] Question 10
Restaurants and cafes could offer internet for free so that people can do work there and have access to internet services.